Industrial Wastewater Solution
Scope of application:
● Various electroplating wastewater treatment, including cyanide containing wastewater, single and mixed heavy metal wastewater containing chromium (Cr), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), nickel (Ni), cadmium (Cd), etc;
● PCB circuit board wastewater treatment;
● Other wastewater containing heavy metals.
Technical principles:
The equipment takes functional nano Ceramic membrane as the core element, uses the nano pore filtration technology on the surface of Ceramic membrane and the binding force of the nano pore double electric layer in the membrane to intercept heavy metals; Adopting a unique operating mode to slow down membrane blockage. During the treatment process, flocculants such as iron and aluminum series and polymer coagulants such as PAM are not added, resulting in high heavy metal content and easy dehydration of the sludge. It can be directly recycled and utilized as a resource.
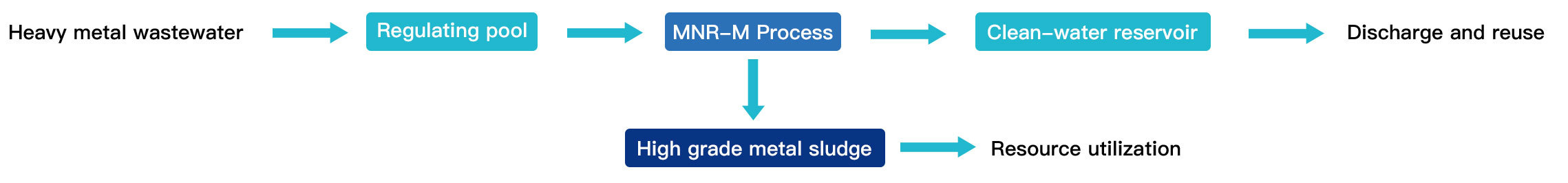
Product advantages:
● Without adding flocculants or coagulants, the metal content in sludge is high, which is conducive to resource recovery and utilization;
● Unified treatment of heavy metal mixed wastewater such as copper (Cu), nickel (Ni), chromium (Cr), zinc (Zn), cadmium (Cd);
● The heavy metal content in the effluent meets the standards in Table 3, and the operation is stable and reliable;
● Functional nano Ceramic membrane is adopted, with a service life of more than 20 years; Integrated equipment, fully automatic control, remote monitoring;
● Advanced technology, high efficiency, and small footprint.

A certain electroplating wastewater treatment station in Xinxiang, Henan(240 m3/d,Including comprehensive wastewater treatment)

A certain electroplating wastewater treatment station in Yangzhou(660 m3/d )
MNR-M integrated heavy metal wastewater treatment equipment covers an area of land
| Number | Processing scale[m3/d] | MNR Process footprint [m2] |
| 1 | 50 | 24 |
| 2 | 100 | 27 |
| 3 | 150 | 30 |
| 4 | 200 | 52 |
| 5 | 300 | 60 |
| 6 | 500 | 100 |
Comparison between MNR-M process and traditional process technology
| Project | Traditional processing technology | MNR Process |
| Effluent quality | Unstable and difficult to meet new standards | Stable reaching new standards |
| Reuse difficulty | Adding PAM, difficult to reuse | Easy to reuse |
| Operating cost | A | 50~70%A |
| Cover an area of | B | 30~50%B |
| Labor intensity | Tall | Low, unmanned operation |
| Sludge situation | C,Difficulty in resource utilization | 30~40%C,Easy resource utilization |
Comparison of Resource Utilization between MNR-M Process and Traditional Process
| Serial Number | Project | Traditional treatment process sludge | MNR Process sludge | ||
| Content[mg/kg] | Dry weight[%] | Content[mg/kg] | Dry weight[%] | ||
| 1 | Fe | 71670 | 7.17 | 51095 | 5.11 |
| 2 | Cu | 14420 | 1.44 | 47575 | 4.76 |
| 3 | Zn | 57515 | 5.75 | 97920 | 9.79 |
| 4 | Ni | 57030 | 5.70 | 109620 | 10.96 |
| 5 | Cr | 39570 | 3.96 | 72140 | 7.21 |
Comparison of effluent results between MNR-M treatment process and traditional treatment process
| Serial Number | Project | Comprehensive wastewater | Traditional treatment process effluent | MNR Effluent | Emission standard | ||
| Table 3 | Table 2 | Table 1 | |||||
| 1 | Ni [mg/L] | 200.5 | 0.38 | 0.031 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1 |
| 2 | cu[mg/L] | 184.6 | 0.37 | 0.133 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1 |
| 3 | Cr [mg/L] | 84.35 | 0.783 | 0.15 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 |
| 4 | Zn [mg/L] | 76.8 | 0.076 | 0.085 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |



